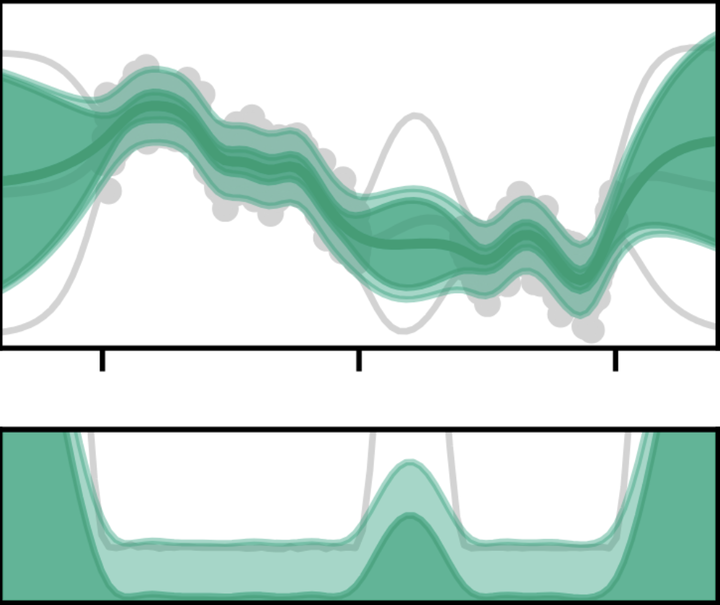
 Computation-aware Gaussian process posterior with learned sparse actions after training.
Computation-aware Gaussian process posterior with learned sparse actions after training.Abstract
Model selection in Gaussian processes scales prohibitively with the size of the training dataset, both in time and memory. While many approximations exist, all incur inevitable approximation error. Recent work accounts for this error in the form of computational uncertainty, which enables – at the cost of quadratic complexity – an explicit tradeoff between computation and precision. Here we extend this development to model selection, which requires significant enhancements to the existing approach, including linear-time scaling in the size of the dataset. We propose a novel training loss for hyperparameter optimization and demonstrate empirically that the resulting method can outperform SGPR, CGGP and SVGP, state-of-the-art methods for GP model selection, on medium to large-scale datasets. Our experiments show that model selection for computation-aware GPs trained on 1.8 million data points can be done within a few hours on a single GPU. As a result of this work, Gaussian processes can be trained on large-scale datasets without significantly compromising their ability to quantify uncertainty – a fundamental prerequisite for optimal decision-making.